تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
در ابتدا به توضیح Bandwidth و یا پهنای باند می پردازیم.
پهنای باند به شما می گوید چه مقدار داده در هر زمان از یک منبع منتقل شده است
که در هر زمان داده از نظر منبع چه مقدار داده می تواند منتقل شود.
دانستن نحوه عملکرد و پهنای باند برای عملکرد مدیرانی که امیدوارند
بتوانند تصویری شفاف از عملکرد شبکه خود داشته باشند بسیار مهم است.
پهنای باند شبکه اندازه گیری ای است که نشان دهنده حداکثر ظرفیت یک
اتصال مخابراتی سیمی یا بی سیم برای انتقال داده
از طریق اتصال شبکه در مدت زمان مشخص است.
به طور معمول ، پهنای باند به تعداد بیت ، کیلوبیت ، مگابیت یا گیگابیت
نمایش داده می شود که می تواند در ۱ ثانیه منتقل شود.
پهنای باند مترادف با ظرفیت ، سرعت انتقال داده را توصیف می کند.
Bandwidth و یا پهنای باند
هرچه پهنای باند اتصال داده بیشتر باشد ، داده بیشتری می تواند
همزمان ارسال و دریافت کند. در مفهوم ، پهنای باند را می توان
با حجم آبی که می تواند از طریق یک لوله جریان داشته باشد مقایسه کرد.
هرچه قطر لوله بیشتر باشد ، آب بیشتری می تواند همزمان از آن عبور کند.
پهنای باند بر اساس همان اصل کار می کند. هرچه ظرفیت پیوند
ارتباطی بیشتر باشد ، داده های بیشتری می توانند در ثانیه از آن عبور کنند.
اصطلاحات پهنای باند و سرعت اغلب به جای هم
استفاده می شوند اما به درستی استفاده نمی شوند.
اساساً ، سرعت به سرعت انتقال داده ها اطلاق می شود ،
در حالی که تعریف پهنای باند ، ظرفیت آن سرعت است.
برای استفاده مجدد از استعاره آب ، سرعت به این معنی است
که چگونه آب می تواند به سرعت از طریق لوله هل داده شود.
پهنای باند به مقدار آب قابل انتقال از طریق لوله در یک بازه زمانی مشخص اشاره دارد.
Throughput چیست
Throughput چیست
در اینجا به توضیح مفهوم Throughput می پردازیم.
توان عملیاتی میزان واقعی ترافیک است که شما هنگام اندازه گیری
در زمان واقعی یا سرعت تحویل داده ها در یک بازه زمانی خاص انجام می دهید.
این را می توان در بسته های ثانیه ، بایت در ثانیه یا بیت در ثانیه اندازه گیری کرد.
توان سیستم یا توان کل یعنی مجموع نرخ داده هایی که به همه پایانه ها
که در یک شبکه تحویل داده شده است.
توان عملیاتی یک معیار عملی به حساب می آید.
Throughput اطلاعاتی مربوط به داده ها همچنین اطلاعاتی درباره
تعداد بسته های (packet) در حال رسیدن به مقصد مورد نظر، به کاربر می دهد.
اگر و بسته های حاوی اطلاعات به مقدار زیاد در مسیر رسیدن به مقصد از بین بروند
عملکرد شبکه کاهش می یابد.
پس توجه به Throughput برای بررسی علملکرد لحظه ای شبکه لازم است.
در اینجا این سوال پیش می آید که تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
در ادامه با ما همراه باشید.
تفاوت Throughput و bandwidth
عملکرد throughput و bandwidth مشابه به نظر می رسد،
اما در درواقع عملکردی جدا از هم دارند.
در یک شبکه، برای تعیین این که چه حجمی از بسته های اطلاعاتی
به چه مقدار پهنای باند نیاز دارند تا بتوانند بین دستگاه های موجود
به صورت همزمان ارسال و دریافت شوند. مقدار throughput و یا توان عملیاتی
این مفهوم را می رساند که چه مقدار پکت های اطلاعاتی در حال انتقال در شبکه هستند.
حال برای رسیدن به پاسخ تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
می توان اینگونه بیان کرد که bandwidth، حداکثر داده های ارسالی که می تواند انتقال پیدا کند
را به صورت تئوری در اختیار ما می گذارد. throughput، اطلاعاتی
را در درباره ی تعداد پکت های اطلاعاتی که به سلامت و موفقیت
به مقصد رسیده است را می گوید. پس با توجه به مطالب گفته شده
می توان دریافت که بررسی throughput برای تعیین عملکرد
شبکه برای انتقال داده ها مهم تر از bandwidth است.
اما این مطلب به این معنی نیست که
bandwidth یا پهنای باند هیچ تاثیری بر روی عملکرد شبکه ندارد.
bandwidth بر روی سرعت انتقال داده ها تاثیر دارد.

تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
تفاوت Throughput و Bandwidth در چیست؟
برای مثال پهنای باند کابل شبکه مورد نظر شما ۱۰۰ مگابیت بر ثانیه می باشد ُ
این یعنی این کابل شبکه در هر ثانیه حداکثر می تواند ۱۰۰ مگابیت
پکت های اطلاعاتی را در یک ثانیه از خود عبور دهد.
لازم به ذکر است که واحد اندازه گیری به کار برده شده به عنوان مثال است.
واحد های زمانی مانند Bit Per Second همان بیت در ثانیه ،
Kilobit Per Second همان کیلوبیت در ثانیه و حتی Gigabit Per Second یا گیگابیت بر ثانیه
به کار برده می شود. علامت های اختصار این واحدها به صورت Bps,Kbps,Mbps,Gbps می باشد.
در اینجا لازم دیدیم اطلاعاتی درباره کابل کشی شبکه
که بی ربط با پهنای باند نمی باشد بیان کنیم.

تفاوت Throughput و bandwidth چیست
نکات مهم در کابل کشی شبکه
در این مقاله می خواهیم به بررسی نکات مهم در کابل کشی شبکه به صورت استاندارد و ساختار یافته بپردازیم.
یکی از مواردی بسیار مهم که در بازدهی و کیفیت و سرعت ارتباطات
و مدیریت و نگهداری و طول عمر شبکه های محلی تاثیر فراوانی می گذارد کابل کشی اصولی است.
برای انجام کابل کشی ساختار یافته نیاز به رعایت یکسری اصول
و طی کردن مراحلی است تا نتیجه مطلوب و بدون مشکل حاصل شود.
۱)نقشه کابل کشی
در قدم اول باید در محل حضور پیدا کرده و محل کابل کشی را بازدید کنید.
ابتدا محل قرار گیری رک ها و یا در صورت امکان محل اتاق سرور مشخص شود.
برای انتخاب محل رک و اتاق سرور باید یکسری شرایط لحاظ شود
تا یک اتاق سرور خوب داشته باشیم تا از بروز مشکلات در آینده جلوگیری شود .
سپس باید محل قرار گیری Node ها با شماره بر روی نقشه مشخص شود
تا در هنگام اجرای پروژه بتوان به راحتی پچ پنل و پریزها و موارد دیگر را
به راحتی شماره گذاری کرد و سپس مسیر عبو کابل ها بر روی نقشه مشخص شود
عدم استفاده از نقشه کابل کشی مثل رانندگی بدون مقصد است.
استفاده از نقشه یک دید کلی می دهد که باعث می شود مشکلاتی که ممکن است
در آینده با آن مواجه شویم را پیش بینی کنیم.
برای مطالعه ادامه مقاله کلیک کنید.
سوئیچ شبکه انکاتک POE مدل PSE3224S
سوئیچ شبکه انکاتک POE مدل PSE3224S دارای ۲۶ پورت ،
۲۴ پورت با سرعت ۱۰/۱۰۰/۱۰۰۰ و قابلیت POE که این امر موجب افزایش امنیت
شبکه می شود به این صورت که از تجهیزات شبکه در برابر نوسانات
برق محافظت می کند . این سوئیچ از سوئیچ های شرکت انکاتک است
که تمام سوئیچ های تولید شده آن از قابلیت POE پشتیبانی می کنند .
از ویژگی های دیگر این محصول می توان به پهنای باند
سوئیچینگ ۵۲ Gbps ، پشتیبانی از استاندارد IEEE802.3af/at POE ،
ابعاد ۴۴۰*۲۲۰*۴۴mm ، توان تولیدی ۳۵۰W ، انتقال تصویر و اطلاعات
تا ۱۰۰ متر و همچنین دارای گوشواره هایی است
که امکان نصب در رک ها را ایجاد می کند ، اشاره کرد .
برای مشاهده مشخصات فنی این سوئیچ کلیک کنید.

سوئیچ شبکه انکاتک POE مدل PSE3224S
What is network bandwidth?
Network bandwidth is a measurement indicating the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to transmit data over a network connection in a given amount of time. Typically, bandwidth is represented in the number of bits, kilobits, megabits or gigabits that can be transmitted in 1 second. Synonymous with capacity, bandwidth describes data transfer rate. Bandwidth is not a measure of network speed — a common misconception.
How does bandwidth work?
The more bandwidth a data connection has, the more data it can send and receive at one time. In concept, bandwidth can be compared to the volume of water that can flow through a pipe. The wider the pipe’s diameter, the more water can flow through it at one time. Bandwidth works on the same principle. The higher the capacity of the communication link, the more data can flow through it per second.
The cost of a network connection goes up as bandwidth increases. Thus, a 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) link will be more expensive than one that can handle 250 megabits per second (Mbps) of throughput.
Bandwidth vs. speed
The terms bandwidth and speed are often used interchangeably but not correctly. The cause of the confusion may be due, in part, to advertisements by internet service providers (ISPs) that conflate the two by referring to greater speeds when they truly mean bandwidth.
Essentially, speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted, while the definition of bandwidth is the capacity for that speed. To use the water metaphor again, speed refers to how quickly water can be pushed through a pipe; bandwidth refers to the quantity of water that can be moved through the pipe over a set time frame.
Why bandwidth is important
Bandwidth is not an unlimited resource. In any given deployment location, such as a home or business, there is only so much capacity available. Sometimes, this is due to physical limitations of the network device, such as the router or modem, cabling or wireless frequencies being used. Other times, bandwidth is intentionally rate-limited by a network administrator or internet or wide area network (WAN) carrier.
Multiple devices using the same connection must share bandwidth. Some devices, such as TVs that stream 4K video, are bandwidth hogs. In comparison, a webinar typically uses far less bandwidth. Although speed and bandwidth are not interchangeable, greater bandwidth is essential to maintain tolerable speeds on multiple devices. To help illustrate this, here’s the average bandwidth consumed for various services:
How to measure bandwidth
While bandwidth is traditionally expressed in bits per second (bps), modern network links now have far greater capacity, which is why bandwidth is now more often expressed as Mbps or Gbps.
Bandwidth connections can be symmetrical, which means the data capacity is the same in both directions — upload and download — or asymmetrical, which means download and upload capacity are not equal. In asymmetrical connections, upload capacity is typically smaller than download capacity; this is common in consumer-grade internet broadband connections. Enterprise-grade WAN and DIA links more commonly have symmetrical bandwidth.
Considerations for calculating bandwidth
Technology advances have made some bandwidth calculations more complex, and they can depend on the type of network link being used. For example, optical fiber using different types of light waves and time-division multiplexing can transmit more data through a connection at one time compared to copper Ethernet alternatives, which effectively increases its bandwidth.
In mobile data networks, such as Long-Term Evolution, or LTE, and ۵G, bandwidth is defined as the spectrum of frequencies that operators can license from the Federal Communications Commission and the National Telecommunications and Information Administration for use in the U.S. This spectrum cannot be legally used by anyone other than the business that owns the license to it. The carrier can then use wireless technologies to transport data across that spectrum to achieve the greatest bandwidth the hardware can provide.
bandwidth
Wi-Fi spectrum, on the other hand, is considered to be unlicensed. Thus, anyone with a Wi-Fi access point (AP) or Wi-Fi router can create a wireless network. The caveat is that the spectrum is not guaranteed to be available. Thus, Wi-Fi bandwidth can suffer when there are other Wi-Fi APs attempting to use some or all of the same frequencies.
bandwidth
Effective bandwidth — which is the highest reliable transmission rate a link can provide on any given transport technology — can be measured using a bandwidth test. During a bandwidth test, the link’s capacity is determined by repeatedly measuring the time required for a specific file to leave its point of origin and successfully download at its destination.
After determining bandwidth consumption across the network, it is then necessary to see where applications and data reside and calculate their average bandwidth needs for each user and session.
bandwidth
To understand how much bandwidth a network uplink or internet broadband requires, follow these four steps:
- Determine which applications will be in use.
- Determine the bandwidth requirements of each application.
- Multiply the application requirements of each application by the number of expected simultaneous users.
- Add all application bandwidth numbers together.
what Throughput
In general terms, throughput is the rate of production or the rate at which something is processed.
When used in the context of communication networks, such as Ethernet or packet radio, throughput or network throughput is the rate of successful message delivery over a communication channel. The data these messages belong to may be delivered over a physical or logical link, or it can pass through a certain network node. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second (bit/s or bps), and sometimes in data packets per second (p/s or pps) or data packets per time slot.
Throughput
The system throughput or aggregate throughput is the sum of the data rates that are delivered to all terminals in a network.[1] Throughput is essentially synonymous to digital bandwidth consumption; it can be analyzed mathematically by applying the queueing theory, where the load in packets per time unit is denoted as the arrival rate (λ), and the throughput, where the drop in packets per time unit, is denoted as the departure rate (μ).
The throughput of a communication system may be affected by various factors, including the limitations of underlying analog physical medium, available processing power of the system components, and end-user behavior. When various protocol overheads are taken into account, useful rate of the transferred data can be significantly lower than the maximum achievable throughput; the useful part is usually referred to as goodput
Throughput and bandwidth difference
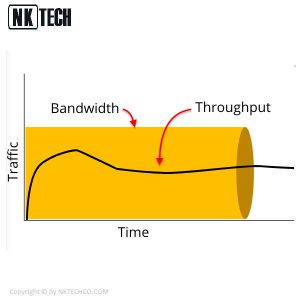
The difference between bandwidth and throughput isn’t necessarily simple. They tell you two different things about the data in your network, but they’re closely related. You can think of bandwidth as a tube and data throughput as sand. If you have a large tube, you can pour more sand through it at a faster rate. Conversely, if you try to put a lot of sand through a small tube, it will go very slowly.
In short, throughput and bandwidth are two different processes with two different goals both contributing to the speed of a network. Data throughput meaning is a practical measure of actual packet delivery while bandwidth is a theoretical measure of packet delivery. Throughput is often a more important indicator of network performance than bandwidth because it will tell you if your network is literally slow or just hypothetically slow.
Best Tools for Monitoring Bandwidth and Throughput
I’ve identified a few key products capable of performing somewhat different functions around monitoring and managing bandwidth and throughput on your networks. Check out this list of top bandwidth tools to better understand which ones might be most helpful for your admin efforts.
۱٫ Network Performance Monitor (Free Trial)
Network Performance Monitor (NPM) from SolarWinds is a tried-and-true, multi-vendor network monitoring system specially designed for scalability. NPM offers a wide range of tools for monitoring and analyzing network performance, advanced alerting, reporting, and problem diagnosis.
Bandwidth:
It is defined as the potential of the data that is to be transferred in a specific period of time. It is the data carrying capacity of the network/transmission medium.
Throughput:
It is the determination of the amount of data is transmitted during a specified time period via a network, interface or channel. Also called as effective data rate or payload rate.
Difference between Bandwidth and Throughput:
| S.No. | Comparison | Bandwidth | Throughput |
|---|---|---|---|
| ۱٫ | Basic | Data capacity is travelled via a channel. | Practical measure of the amount of data actually transmitted through a channel. |
| ۲٫ | Measured in | Bits | Average rate is measured depending on bandwidth. It is measured in terms of bits transferred per second (bps). |
| ۳٫ | Concerned with | Transfer of data by some means. | Communication between two entities |
| ۴٫ | Relevance to layer | Physical layer property. | Work at any of the layers in the OSI model. |
| ۵٫ | Dependence | Not depend on the latency. | It depends on the latency. |
| ۶٫ | Definition | It refers to the maximum amount of the data that can be passed from one point to another. | It is considered as the actual measurement of the data that is being moved through the media at any particular time. |
| ۷٫ | Effect | It is not affected by physical obstruction because it is a theoretical unit to some extent. | It can be easily affected by change in interference, traffic in network, network devices, transmission errors and the host of other type. |
| ۸٫ | Real world Example(Water Tap Example). | It is the speed of tap at which water is coming out. | It is the total amount of water that comes out. |

